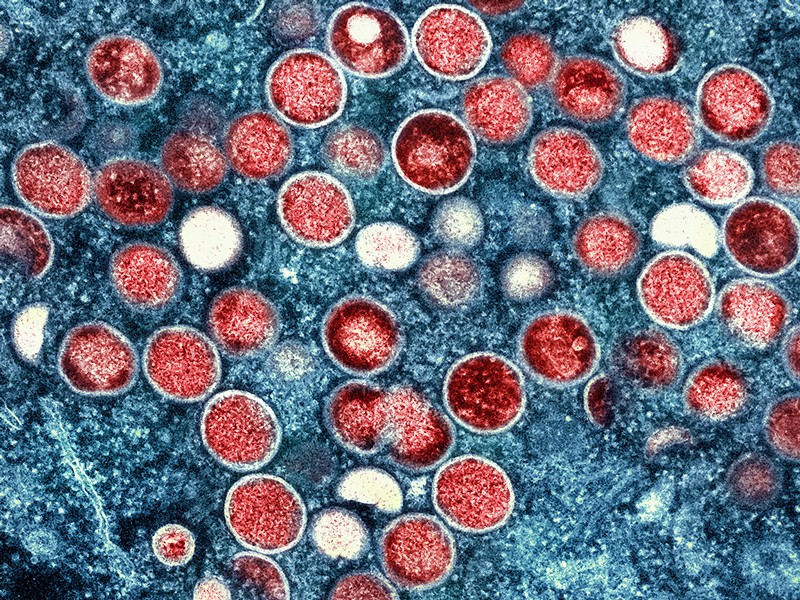
As worldwide monkeypox cases keep on taking off, scientists are diving deeper into how the illness is spreading. Early expectations that the infection sends essentially through rehashed skin-to-skin contact between individuals have generally borne out, as indicated by a tranche of new investigations.
"At the point when you set up this multitude of studies, we see that the clinical show wherever is comparative — yet additionally astounding," says Oriol Mitjà, an irresistible sickness scientist at Germans Trias I Pujol University Hospital in Barcelona, Spain, who co-wrote one of the new examinations in The Lancet1. That is on the grounds that the side effects and example of spread don't seem to be something scientists had seen in West and Central Africa, where the monkeypox infection has caused detached, tenacious flare-ups for a really long time.
Since early May, monkeypox has spread to in excess of 90 nations and prompted in excess of 32,000 diseases, with almost 33% of cases revealed in the United States. The infection's fast spread drove the World Health Organization to give its most elevated level general wellbeing alert on 23 July; US President Joe Biden went with the same pattern on 4 August by pronouncing a US general wellbeing crisis.
Albeit a few ladies and youngsters have been contaminated since May, most cases have up until this point happened in men who have intercourse with men (MSM), particularly those with numerous sexual accomplices or who have mysterious sex. The infection has most likely been exploiting thick sexual organizations in the MSM people group to spread productively, Mitjà says. The more the infection keeps on spreading, the more open doors it should taint different populaces, including wild creatures — which researchers have cautioned could lay out viral repositories that could contaminate people over and over.
'Abounding with infection's
At the point when an individual agreements monkeypox, they can foster influenza like side effects, broadened lymph hubs and unmistakable liquid filled injuries on their skin. Albeit a few scientists have proposed that the monkeypox infection could spread through respiratory beads or airborne particles, as SARS-CoV-2 does, Mitjà and his partners report that examples, taken when an individual is analyzed, from skin sores contain considerably more popular DNA than do those from the throat1. The sores appear to be nearly "overflowing with infection", says Boghuma Titanji, an irresistible illness doctor at Emory University in Atlanta, Georgia, who was not associated with the review.
A few studies2,3, including Mitjà's, show that couple of individuals contract the sickness from a tainted family part with whom they didn't have sexual contact. This finding, matched with the information about viral burden, proposes that respiratory drops and airborne particles presumably aren't the essential transmission course, Titanji says. On the off chance that supported by additional examination, it could raise doubt about whether individuals ought to disengage for the whole span of contamination, which may be troublesome on the grounds that the sickness appears to require as long as a month to determine, she adds.
As yet missing are nitty gritty information about how an individual's viral burden changes over the long run, says Jessica Justman, an irresistible illness doctor at Columbia University in New York City. Despite the fact that Mitjà and his associates didn't recognize a lot of viral DNA in examples that they gathered from individuals' throats right on time during contamination, it's conceivable that assuming they had gathered them later — or much prior — viral levels might have been higher, she says. Such information, which the group is presently gathering in a subsequent report, would permit general wellbeing authorities to offer better confinement and treatment direction to tainted individuals.
Discussing sex
Whether monkeypox is physically sent in outright terms — passed starting with one individual then onto the next through blood, semen or other natural liquids during sex — is as yet hazy. However, a few examinations have tracked down that DNA from the monkeypox infection is available in an individual's semen for quite a long time after they become infected2,3. One concentrate likewise disconnected irresistible infection from a solitary person's semen six days after their side effects appeared4.
Regardless of whether the infection can be physically sent, it's muddled how enormous of a job this method of transmission has, contrasted and essentially being right up front, skin-to-skin contact with an individual or breathing in their respiratory particles — which likewise happen during sex. Assuming different examinations find irresistible infection in semen, understanding how long it can endure in that natural liquid will be significant. Infections, for example, Ebola can continue in semen for quite a long time, on the off chance that not years, after disease, which has muddled endeavors to forestall flare-ups. Until analysts know more, the UK Health Security Agency prescribes that individuals ought to keep on involving condoms for a very long time after contamination
Mitjà and that's what his partners saw, in individuals they analyzed, having a bigger number of sores in the mouth and throat was connected to oral sex, and having more sores in and around the butt was connected to butt-centric open sex. Considering this large number of discoveries, Titanji says it's urgent that general wellbeing authorities don't avoid discussing sex in their direction and are unequivocal about the sorts of security accessible.
More information from thoroughly planned examinations can't come quickly enough, Justman says. A few scientists as of now stress that the episode is beyond the reason behind being contained, given insight about lacking immunization reserves and unavailable antiviral medicines, as well as inadequate testing. Financing and inspiration to study monkeypox are restricted contrasted and COVID-19, she says. "We don't have an 'Activity Warp Speed'," like there was to fire up US immunization advancement during the pandemic, she adds.


0 Comments